ReentrantLock 和 公平锁
ReentrantLock 是基于 Lock 实现的可重入锁,所有的 Lock 都是基于 AQS 实现的。
AQS是通过将每条请求共享资源的线程封装成一个节点来实现锁的分配。
它的可重入是因为实现了同步器 Sync,这个抽象类 Sync 继承了AQS,在 Sync 的两个实现类中,包括了公平锁和非公平锁。
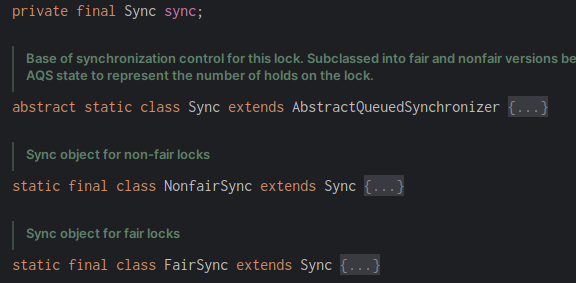
同步器 Sync 继承自 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 抽象队列同步器
ReentrantLock默认是非公平锁,在构造函数中传入true 构建公平锁
1public ReentrantLock() {2 sync = new NonfairSync();3}4
5public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {6 sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();7}一般情况下并不需要公平锁,除非你的场景中需要保证顺序性
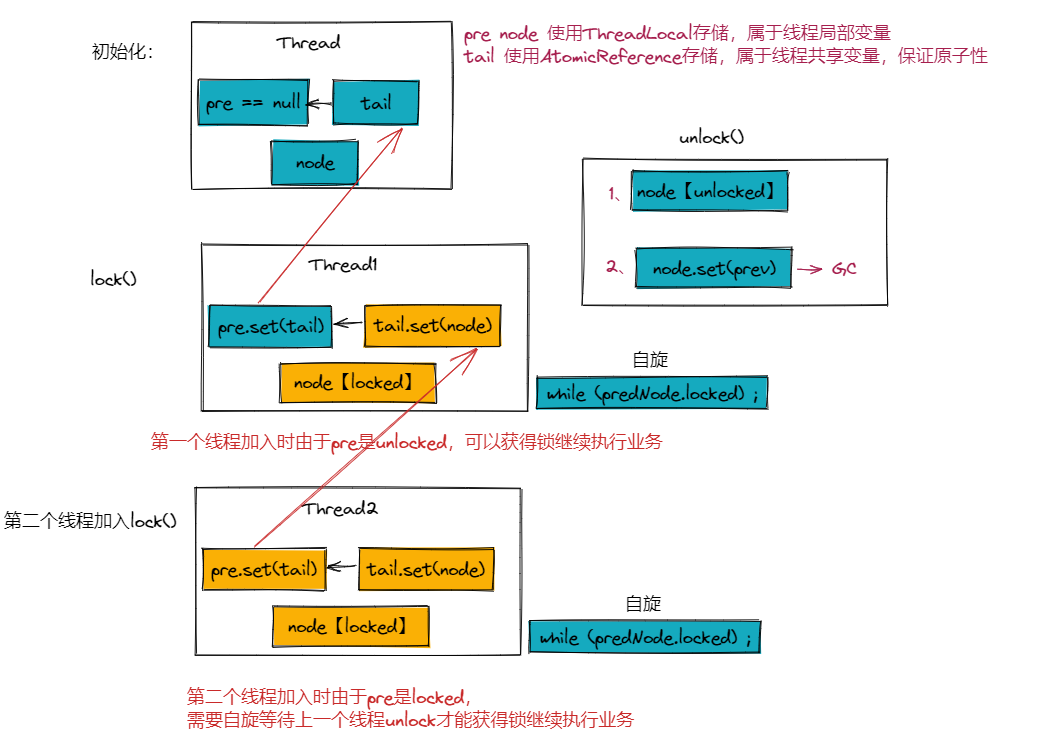
CLH 基于单向链表的公平锁
1public class CLHLock implements Lock {2
3 private final ThreadLocal<CLHLock.Node> prev;4 private final ThreadLocal<CLHLock.Node> node;5 private final AtomicReference<CLHLock.Node> tail = new AtomicReference<>(new CLHLock.Node());6
7 public CLHLock() {8 this.prev = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> null);9 this.node = ThreadLocal.withInitial(CLHLock.Node::new);10 }11
12
13 private static class Node {14 private volatile boolean locked;15 }22 collapsed lines
16
17 @Override18 public void lock() {19 final Node node = this.node.get();20 node.locked = true;21 //把新加入的结点设置成尾部结点22 //getAndSet 获取当前值并设置新值23 Node predNode = this.tail.getAndSet(node);24 this.prev.set(predNode);25 //自旋26 while (predNode.locked) ;27 }28
29 @Override30 public void unlock() {31 final Node node = this.node.get();32 node.locked = false;33 this.node.set(this.prev.get());34 }35
36 ...37}MCS
和CLH一样也是一种基于链表的可扩展、高性能、公平的自旋锁
不同点:它是真的有下一个节点 next,添加这个真实节点后,它就可以只在本地变量上自旋,而 CLH 是前驱节点的属性上自旋。
CLH 更需要线程数据在同一块内存上效果才更好— SMP 架构
MCS 更适合 NUMA 非一致存储访问架构,无论数据是否分散在不同的CPU模块都没有影响
1public class MCSLock implements Lock {2 private AtomicReference<MCSLock.Node> tail = new AtomicReference<>(null);3
4 private ThreadLocal<MCSLock.Node> node;5
6 private static class Node {7 private volatile boolean locked = false;8 private volatile Node next = null;9 }10
11 public MCSLock() {12 this.node = ThreadLocal.withInitial(Node::new);13 }14
15 @Override28 collapsed lines
16 public void lock() {17 Node node = this.node.get();18 Node preNode = tail.getAndSet(node);19 if (null == preNode) {20 node.locked = true;21 return;22 }23 node.locked = false;24 preNode.next = node;25 while (!node.locked) ;26 }27
28 @Override29 public void unlock() {30 Node node = this.node.get();31 if (null != node.next) {32 node.next.locked = true;33 node.next = null;34 return;35 }36 if (tail.compareAndSet(node, null)) {37 return;38 }39 while (node.next == null) ;40 }41
42 ...43}TicketLock
TicketLock 就像你去银行、呷哺给你的一个排号卡一样,叫到你号你才能进去。属于严格的公平性实现,但是多处理器系统上,每个进程/线程占用的处理器都在读写同一个变量,每次读写操作都需要进行多处理间的缓存同步,非常消耗系统性能。
代码实现上也比较简单,lock() 中设置拥有者的号牌,并进入自旋比对。unlock() 中使用 CAS 进行解锁操作,并处理移除。
1public class TicketLock implements Lock {2
3 private AtomicInteger serviceCount = new AtomicInteger(0);4 private AtomicInteger ticketCount = new AtomicInteger(0);5 private final ThreadLocal<Integer> owner = new ThreadLocal<>();6
7 @Override8 public void lock() {9 owner.set(ticketCount.getAndIncrement());10 while (serviceCount.get() != owner.get());11 }12
13 @Override14 public void unlock() {15 serviceCount.compareAndSet(owner.get(), owner.get() + 1);5 collapsed lines
16 owner.remove();17 }18
19 ...20}
